Learn how to practice/crack on Java SE 7 Programmer Certification and pass the OCAJP 7 exam 1Z0-803
Oracle Certified Associate - (OCP) Java SE 7 Programmer Certification is basic level certificate for any IT professional working with Java. MyExamCloud® study plan provides complete study guides and practice for OCAJP 7 exams. This traning is designed to help you pass the Oracle Certified Associate Java SE 7 Programmer (OCAJP 7) Certification. Even if you dont have any knowledge in Java platform before, by the end of the MyExamCloud® practice exam you will be able to take the OCAJP 7 exam. Any programming knowledge is no needed and no prior Java programming experience required. With OCAJP 7 (1Z0-803) certification you will be in high demand by many employers and will get a superior salary.
This study plan is specifically designed on helping you to pass the Java SE 7 Programmer I Exam [1Z0-803] exam. All you have to do learn from MyExamCloud® study notes and practice yourself with the MyExamCloud® Practice Test,Mock Exams,Quiz Tests and Flash Card Quiz Exams.
This MyExamCloud® OCAJP 7 study plan was developed by Java Certified Architect and Certified Developer, over 17 years experience in Java applications. Login https://www.myexamcloud.com/onlineexam/viewStudyPlan.html?s=KFx2lAszxQI= today and get your Free 1Z0-803 Java SE 7 Programmer I Practice Mock Exam today!
OCAJP 7 Exam Information
The OCAJP 7 (Oracle Certified Associate, Java SE 7 Programmer) certification improves object-orientated programming and Java fundamental skills.Binary Literals - In Java SE 7, the integral types (byte, short, int, and long) can also be expressed using the binary number system. To specify a binary literal, add the prefix 0b or 0B to the number.
Underscores in Numeric Literals - Any number of underscore characters (_) can appear anywhere between digits in a numerical literal. This feature enables you, for example, to separate groups of digits in numeric literals, which can improve the readability of your code.
Strings in switch Statements - You can use the String class in the expression of a switch statement.
Type Inference for Generic Instance Creation - You can replace the type arguments required to invoke the constructor of a generic class with an empty set of type parameters (< >) as long as the compiler can infer the type arguments from the context. This pair of angle brackets is informally called the diamond.
The try-with-resources Statement - The try-with-resources statement is a try statement that declares one or more resources. A resource is an object that must be closed after the program is finished with it. The try-with-resources statement ensures that each resource is closed at the end of the statement. Any object that implements the new java.lang.AutoCloseable interface or the java.io.Closeable interface can be used as a resource. The classes java.io.InputStream, OutputStream, Reader, Writer, java.sql.Connection, Statement, and ResultSet have been retrofitted to implement the AutoCloseable interface and can all be used as resources in a try-with-resources statement.
Catching Multiple Exception Types and Re-throwing Exceptions with Improved Type Checking - A single catch block
OCAJP 7 Certification Path
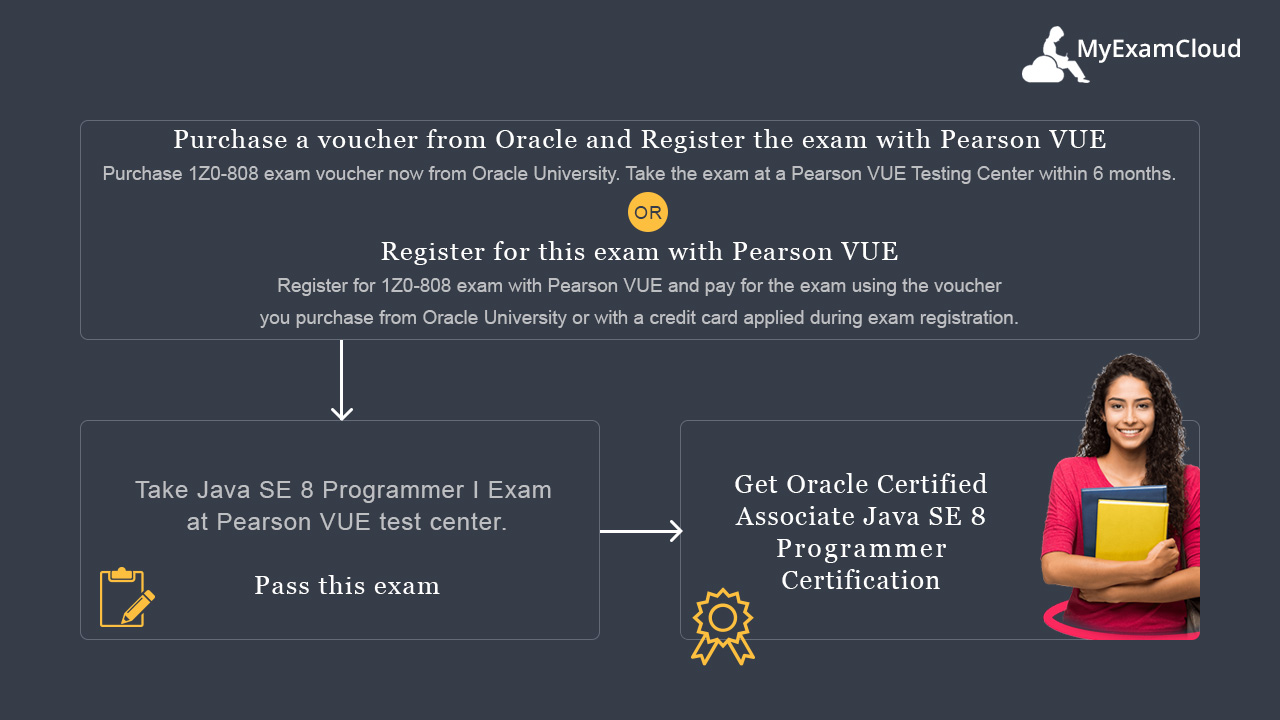 |
OCAJP 7 Certification Path |
OCAJP 7 Topics
Topics Covered by MyExamCloud® OCAJP 7 Study Plan
Java Basics
- Define the scope of variables
- Define the structure of a Java class
- Create executable Java applications with a main method
- Import other Java packages to make them accessible in your code
- Working With Java Data Types
Declare and initialize variables
- Differentiate between object reference variables and primitive variables
- Read or write to object fields
- Explain an Object's Lifecycle (creation, "dereference" and garbage collection)
- Call methods on objects
- Manipulate data using the StringBuilder class and its methods
- Creating and manipulating Strings
- Using Operators and Decision Constructs
Use Java operators
- Use parenthesis to override operator precedence
- Test equality between Strings and other objects using == and equals ()
- Create if and if/else constructs
- Use a switch statement
Creating and Using Arrays
- Declare, instantiate, initialize and use a one-dimensional array
- Declare, instantiate, initialize and use multi-dimensional array
- Declare and use an ArrayList
Using Loop Constructs
- Create and use while loops
- Create and use for loops including the enhanced for loop
- Create and use do/while loops
- Compare loop constructs
- Use break and continue
Working with Methods and Encapsulation
- Create methods with arguments and return values
- Apply the static keyword to methods and fields
- Create an overloaded method
- Differentiate between default and user defined constructors
- Create and overload constructors
- Apply access modifiers
- Apply encapsulation principles to a class
- Determine the effect upon object references and primitive values when they are passed into methods that change the values
Working with Inheritance
- Implement inheritance
- Develop code that demonstrates the use of polymorphism
- Differentiate between the type of a reference and the type of an object
- Determine when casting is necessary
- Use super and this to access objects and constructors
- Use abstract classes and interfaces
Handling Exceptions
- Differentiate among checked exceptions, RuntimeExceptions and Errors
- Create a try-catch block and determine how exceptions alter normal program flow
- Describe what Exceptions are used for in Java
- Invoke a method that throws an exception
- Recognize common exception classes and categories
